simplifying the ITILv4 Change Management Process
Change Management, within the ITIL framework, is a structured approach to managing and controlling changes in an organization’s IT infrastructure. It’s a crucial process that ensures alterations to IT systems are implemented smoothly, minimizing disruptions and aligning with business objectives.
What is Change Management?
ITILv4 (Information Technology Infrastructure Library version 4), change management is a fundamental practice within the Service Transition stage, focusing on controlling and managing changes to IT services, systems, and infrastructure in a structured manner. It aims to ensure that changes are implemented efficiently with minimal disruption to ongoing operations while maximizing the benefits to the organization.
ITILv4’s change management framework involves a series of well-defined processes and procedures to evaluate, authorize, prioritize, and manage changes across the IT landscape. It emphasizes the need for thorough assessment, documentation, and risk analysis of proposed changes to determine potential impacts on services, systems, and associated components.
Key elements of ITILv4’s change management framework include change evaluation, change planning, change authorization, and change implementation. Change evaluation involves assessing proposed changes based on criteria like risk, impact, and cost-benefit analysis. Change planning outlines the steps and resources required for successful implementation. Change authorization ensures that changes are approved by the appropriate stakeholders, while change implementation oversees the execution of approved changes.
ITILv4’s change management aligns IT services with business objectives, enhances service quality, minimizes disruptions, and fosters a more controlled and agile IT environment, enabling organizations to adapt efficiently to evolving business needs and technological advancements.

Why is Change Management Used?
Change management holds a crucial role within ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) due to the inherent complexities and rapid evolution of IT services and systems. IT environments are dynamic, constantly evolving to meet new business needs, technological advancements, and changing market demands. Change management within ITIL is utilized for several reasons:
- Minimize Disruptions: ITIL’s change management aims to reduce the impact of changes on ongoing operations and services. By evaluating and planning changes thoroughly, it seeks to minimize disruptions that could arise from implementing modifications in IT infrastructure, systems, or services.
- Risk Mitigation: It assesses and manages the risks associated with implementing changes. This process helps in identifying potential issues before they occur, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate risks, ensuring stability and reliability within the IT environment.
- Improved Service Quality: By implementing changes in a controlled and structured manner, ITIL’s change management helps maintain and improve service quality. It ensures that changes are aligned with business objectives and are implemented without compromising the performance and reliability of IT services.
- Regulatory Compliance: In many industries, compliance with regulations and standards is critical. Change management in ITIL ensures that changes follow regulatory requirements and organizational policies, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
- Facilitating Continuous Improvement: Change management promotes a culture of continuous improvement within IT services. It allows for the implementation of feedback and lessons learned from previous changes, fostering an environment where the IT infrastructure is always evolving to better meet business needs.
Ultimately, change management in ITIL is a structured approach that supports the delivery of high-quality IT services, aligning them with the organization’s objectives, minimizing risks, and enabling agility and responsiveness in the face of constant change.
Benefits of Change Management
- Reduced Disruptions: By following a structured process, Change Management minimizes unexpected downtime and errors during changes, leading to increased system stability.
- Alignment with Business Objectives: It ensures that changes support the organization’s goals and strategies, avoiding unnecessary or conflicting alterations.
- Enhanced Communication: Change Management fosters communication among stakeholders, promoting transparency and collaboration.
- Improved Risk Management: It assesses potential risks associated with changes, allowing organizations to make informed decisions and mitigate risks effectively.
Steps in Change Management
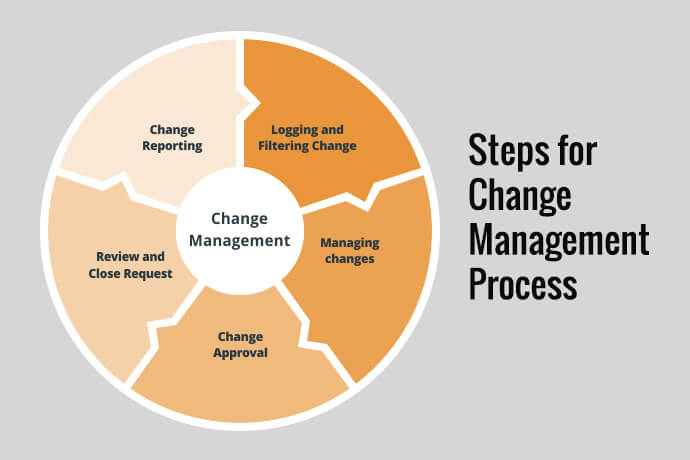
- Request for Change (RFC): The process begins with the submission of an RFC, detailing the proposed change’s scope, impact, and justification.
- Change Evaluation: The change is evaluated based on its potential impact, risks, benefits, and alignment with business objectives.
- Change Approval: The proposed change undergoes review by the Change Advisory Board (CAB) or Change Manager, who approve, reject, or defer the change based on its assessment.
- Change Implementation: If approved, the change is planned, tested, and implemented following predefined procedures to minimize disruption.
- Post-Implementation Review: The change’s impact is monitored and reviewed to ensure it meets the expected outcomes and to identify any unforeseen issues.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Change Manager
The Change Manager is a pivotal role in Change Management, responsible for:
- Overseeing the Change Process: They ensure that changes adhere to policies and procedures.
- Chairing CAB Meetings: The Change Manager leads CAB meetings, facilitating discussions on proposed changes.
- Risk Assessment: They assess risks associated with changes and make decisions regarding change approval.
- Communication: The Change Manager communicates change schedules, progress, and outcomes to stakeholders.
Change Failure: Reasons and Resolution
Change failure occurs when implemented changes do not meet their objectives or cause unexpected disruptions. Reasons for change failure can include poor planning, inadequate testing, lack of stakeholder involvement, or insufficient communication.
To resolve change failure, actions can include:
- Root Cause Analysis: Identifying the underlying reasons for the failure to prevent recurrence.
- Reverting Changes: Rolling back to the previous state if the change has caused severe disruptions.
- Process Improvement: Reviewing Change Management processes to prevent similar failures in the future.
Interview Questions on Change Failure
During interviews for Change Management roles, questions may revolve around:
- Handling Change Failure: How you identify, mitigate, and resolve change failures.
- Risk Assessment: Methods for assessing risks associated with proposed changes.
- Communication Skills: How you communicate with stakeholders during the change process.
you might be Interested in Reading Article on ITIL–



1 comment